Grid in OroCRM is a very convenient way to display information about all or few records of an entity. Default OroCRM has a lot of grids for different entities. OroCRM developers provided a useful and easy way to create grids for a custom entity or display some specific information for default entities.
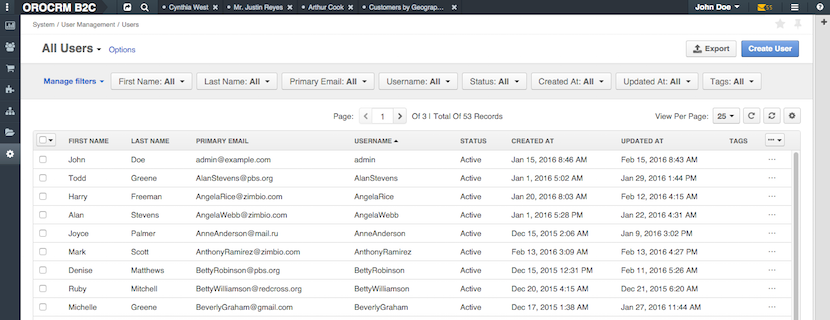
For example, let’s take a look at the users grid:
As you can also see, it is a simple table with rows and columns that contain information about users. Also, the grid includes a list of filters, pagination and some actions. Moreover, each row has few functionalities to view, edit or delete data there. The standard grid control section located at the top includes all those elements. If more detailed:
- Export button – allows to export grid content in CSV format.
- Pagination control – provides information about a grid page itself, records in the grid and total number of pages. Number of pages in the grid depends on its configuration, this parameters can be set in System -> Configuration -> Display settings -> Data Grid settings.
- Grid content controls – allow to change the number of records displayed per page using the View per Page control, refresh grid contents, reset the grid to its default view.
- Filters – are useful when you need to pick up the records that you need from entire data. The filters are located above the grid controls.
We have already reviewed the frontend part of the grid, and now let’s move to its backend side. We’ve took the Users grid as an example. Pay attention that each grid should be configured in the parameters file. This file is located in …Bundle/Resources/config folder, it is called datagrid.yml and has the following structure:
datagrid:
users-grid:
extended_entity_name: %oro_user.entity.class%
options:
entityHint: user
entity_pagination: true
acl_resource: oro_user_user_view
source:
type: orm
query:
select:
- u.id
- u.username
- u.email
- u.firstName
- u.lastName
- u.createdAt
- u.updatedAt
- u.enabled
from:
- { table: %oro_user.entity.class%, alias: u }
inline_editing:
enable: true
columns:
firstName:
label: oro.user.first_name.label
lastName:
label: oro.user.last_name.label
email:
label: oro.user.email.label
username:
label: oro.user.username.label
enabled:
label: oro.user.enabled.label
frontend_type: select
choices:
- Inactive
- Active
createdAt:
label: oro.ui.created_at
frontend_type: datetime
updatedAt:
label: oro.ui.updated_at
frontend_type: datetime
properties:
id: ~
update_link:
type: url
route: oro_user_update
params:
- id
view_link:
type: url
route: oro_user_view
params:
- id
delete_link:
type: url
route: oro_api_delete_user
params:
- id
sorters:
columns:
username:
data_name: u.username
email:
data_name: u.email
firstName:
data_name: u.firstName
lastName:
data_name: u.lastName
createdAt:
data_name: u.createdAt
updatedAt:
data_name: u.updatedAt
enabled:
data_name: u.enabled
default:
username: %oro_datagrid.extension.orm_sorter.class%::DIRECTION_ASC
filters:
columns:
firstName:
type: string
data_name: u.firstName
lastName:
type: string
data_name: u.lastName
email:
type: string
data_name: u.email
username:
type: string
data_name: u.username
enabled:
type: choice
data_name: u.enabled
options:
field_options:
choices:
'false': Inactive
'true': Active
createdAt:
type: datetime
data_name: u.createdAt
updatedAt:
type: datetime
data_name: u.updatedAt
actions:
view:
type: navigate
label: oro.grid.action.view
link: view_link
icon: eye-open
acl_resource: oro_user_user_view
rowAction: true
update:
type: navigate
label: oro.grid.action.update
link: update_link
icon: edit
acl_resource: oro_user_user_update
delete:
type: delete
label: oro.grid.action.delete
link: delete_link
icon: trash
acl_resource: oro_user_user_delete
Now let’s check it more detailed.
Name (Identifier)
The first part of a grid is a name. Previously mentioned users grid has “users-grid” name, it is a unique identifier for the grid in application.
Extends
Almost every grid may be extended: we can use data from a parent grid with necessary adjustments and additions. For that purpose use “extends” configuration node:
user-cases-grid:
extends: cases-grid
source:
query:
where:
and:
- (assignedTo.id = :id OR owner.id = :id)
bind_parameters:
- id
options:
entity_pagination: false
The “user-cases-grid” extends the “cases-grid” and then changes the “source” node, all filters, sorters from parent grid.
Source
There is a specific query to get data from any entity. The grid can receive the data from one entity or join few entities. For example, the users grid uses only one entity:
source:
type: orm
query:
select:
- u.id
- u.username
- u.email
- u.firstName
- u.lastName
- u.createdAt
- u.updatedAt
- u.enabled
from:
- { table: %oro_user.entity.class%, alias: u }
When, for example, the business unit’s grid additionally uses owner’s entity:
source:
acl_resource: oro_business_unit_view
type: orm
query:
select:
- u.id
- u.name
- u.email
- u.phone
- u.createdAt
- owner.name as ownerName
from:
- { table: OroOrganizationBundle:BusinessUnit, alias: u }
join:
left:
owner:
join: u.owner
alias: owner
Columns
This part of a grid setting describes the columns and type of data that are shown in the grid. There should be some unique column identifier and type of data. The default type is a string, check it below:
columns:
firstName:
label: oro.user.first_name.label
lastName:
label: oro.user.last_name.label
email:
label: oro.user.email.label
username:
label: oro.user.username.label
enabled:
label: oro.user.enabled.label
frontend_type: select
choices:
- Inactive
- Active
createdAt:
label: oro.ui.created_at
frontend_type: datetime
updatedAt:
label: oro.ui.updated_at
frontend_type: datetime
Configuration format of the columns is different, depending on the data type. Here is a list of parameters for all types:
- type – backend formatter type (default value: field)
- label – column title (translated on backend, translation should be placed in “messages” domain)
- frontend_type – frontend formatters that process the column value (default value: string)
- editable – is a column editable on frontend (default value: false)
- renderable – should a column be rendered? (default value: true)
- data_name – data identifier (column name suggested by default)
Properties
It is a unique identifier for some value like link, template etc. Property is similar to column, but it does not have a frontend representation.
properties:
id: ~
update_link:
type: url
route: oro_user_update
params:
- id
view_link:
type: url
route: oro_user_view
params:
- id
delete_link:
type: url
route: oro_api_delete_user
params:
- id
Sorters
It is used for making the grid’s columns sortable.
sorters:
columns:
username:
data_name: u.username
email:
data_name: u.email
firstName:
data_name: u.firstName
lastName:
data_name: u.lastName
createdAt:
data_name: u.createdAt
updatedAt:
data_name: u.updatedAt
enabled:
data_name: u.enabled
default:
username: %oro_datagrid.extension.orm_sorter.class%::DIRECTION_ASC
Filters
In this node we describe the list of grid’s filters and types.
filters:
columns:
firstName:
type: string
data_name: u.firstName
lastName:
type: string
data_name: u.lastName
email:
type: string
data_name: u.email
username:
type: string
data_name: u.username
enabled:
type: choice
data_name: u.enabled
options:
field_options:
choices:
'false': Inactive
'true': Active
createdAt:
type: datetime
data_name: u.createdAt
updatedAt:
type: datetime
data_name: u.updatedAt
Actions
It describes the list of row’s actions. In our users grid example, we can see that actions use the parameters that we’ve described in the parameters node (view_link, update_link, delete_link).
actions:
view:
type: navigate
label: oro.grid.action.view
link: view_link
icon: eye-open
acl_resource: oro_user_user_view
rowAction: true
update:
type: navigate
label: oro.grid.action.update
link: update_link
icon: edit
acl_resource: oro_user_user_update
delete:
type: delete
label: oro.grid.action.delete
link: delete_link
icon: trash
acl_resource: oro_user_user_delete
On the frontend part, the grid is displayed by the specific macros. We only need to set name (identifier) of this grid.
{% import 'OroDataGridBundle::macros.html.twig' as dataGrid %}
{% block content %}
{{ dataGrid.renderGrid(users-grid) }}
{% endblock %}
Also, there is a possibility to pass the additional grid query parameters. Let’s check the standard “user-cases-grid”:
{{ dataGrid.renderGrid('user-cases-grid', {id: entity.id}) }}
And its backend part:
user-cases-grid:
extends: cases-grid
source:
query:
where:
and:
- (assignedTo.id = :id OR owner.id = :id)
bind_parameters:
- id
options:
entity_pagination: false
It uses a specific “bind_parameters” node for parameters binding.
In case if names of parameters in the grid and query do not match, you can pass an associative array of parameters where the key is the name of parameter in the query and a value is the name of parameter:
query:
where:
and:
- (assignedTo.id = :user_id OR owner.id = :user_id)
bind_parameters:
user_id: id
As you can see, the functionality of OroDataGridBundle is really powerful. We do not need to write a lot of code, just customize columns, add actions, sorters and different type of filters. It makes the development process more productive and handy.