Magento vs Oracle Commerce Cloud — both are powerful, enterprise-level eCommerce platforms, but each caters to different business needs. Magento (Adobe Commerce) is renowned for its extensive customization options, making it a go-to solution for businesses requiring control over every aspect of their online store.

Oracle Commerce, meanwhile, is designed to handle complex B2B transactions, with an emphasis on automation, integration with enterprise systems, and seamless multi-site management.
When evaluating Magento alternatives like Oracle Commerce Cloud, businesses should consider their priorities, such as customization flexibility or enterprise integration capabilities. Selecting the right eCommerce platform is essential for businesses looking to scale and streamline their operations. This guide will walk you through the key differences between Magento and Oracle Commerce, helping you determine which platform is best suited for your specific business needs.
Magento/ Adobe Commerce vs Oracle Commerce – A 2024 Comparison Guide
Core Functionality and Features
Choosing the right eCommerce platform is crucial for the growth and efficiency of an online business. Both Magento and Oracle Commerce offer a range of essential features, but they are targeted at different business sizes and needs.
Magento
Magento is well-known for its flexibility and robust feature set. It offers businesses advanced multi-store management, the ability to support both B2B and B2C operations, and highly customizable product catalogs. With Magento’s modular architecture, businesses can integrate third-party extensions and customize their workflows, making it a favorite for enterprises that need to handle complex eCommerce operations.
Magento’s custom checkout processes and extensive catalog management capabilities make it highly versatile for businesses across industries.
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce, on the other hand, excels in automating business processes and handling complex B2B eCommerce transactions. The platform is optimized for multi-site management, with built-in tools for personalization and customer experience management. Oracle’s deep integration capabilities with other enterprise systems like ERP and CRM solutions make it an excellent choice for businesses focused on automation and seamless enterprise-level integration.
Oracle also shines in its automation upgrades and B2B-specific functionalities, which help streamline operations for large-scale enterprises.
Magento offers more flexibility and customization options, while Oracle Commerce provides stronger built-in automation and enterprise integration, making it ideal for large businesses focused on B2B operations
Ease of Use and User Interface (UI)
The Magento vs Oracle Commerce comparison in ease of use shows significant differences. Magento provides a powerful but complex interface that requires technical knowledge, while Oracle Commerce Cloud offers a more streamlined, fully hosted solution with a simpler interface. This makes Oracle more appealing to enterprises seeking easier management without the need for extensive development resources.
Magento
When it comes to ease of use, Magento offers an extensive range of features, but this flexibility comes with a steeper learning curve. Magento Open Source in particular requires technical knowledge to set up and manage effectively, especially when dealing with complex customizations or multi-store setups.
Even with Adobe Commerce, which simplifies some of these tasks, Magento generally requires developer resources to maximize its capabilities. The platform’s advanced features make it a powerful solution, but it can be overwhelming for non-technical users without dedicated support or technical expertise.
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce, on the other hand, is designed to simplify many of the processes involved in managing an eCommerce platform. Its cloud-based infrastructure means that upgrades, patches, and performance enhancements happen automatically, reducing the need for manual intervention. Oracle’s user interface is more intuitive, and the platform focuses on B2B ease of use, offering streamlined workflows for managing product catalogs, orders, and customer accounts.
Automation is a key strength of Oracle Commerce, making it easier for businesses to manage operations without requiring extensive technical involvement.
Magento offers more flexibility but requires technical expertise to manage effectively. Oracle Commerce provides a more streamlined user experience with built-in automation, making it easier for businesses to manage day-to-day operations without heavy technical oversight.
Performance and Scalability
For performance and scalability, the Magento vs Oracle Commerce Cloud debate highlights Magento’s ability to scale through custom solutions and third-party hosting providers, making it ideal for businesses needing high levels of control. Oracle Commerce Cloud, being a fully hosted solution, offers built-in scalability, allowing businesses to grow without having to manage their own infrastructure, which simplifies operations for large enterprises.
Magento
Magento is built for performance and scalability, especially for businesses that expect to handle large volumes of traffic and extensive product catalogs. As a self-hosted platform, businesses have full control over performance optimizations such as caching, content delivery networks (CDNs), and server configurations.
This gives Magento users the ability to fine-tune performance to meet the specific demands of their stores, making it ideal for large enterprises with high traffic volumes or complex global operations. However, this level of control also requires dedicated technical resources to manage and optimize.
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce, being a fully cloud-hosted solution, automates much of the performance management process. Oracle’s cloud infrastructure allows for automatic scaling to accommodate traffic spikes and increased demand without requiring manual intervention. Performance optimization happens in the background, which makes the platform especially appealing for businesses that don’t want to manage their own infrastructure.
This makes Oracle Commerce a strong option for enterprises with global operations that need a reliable, scalable eCommerce solution without the complexity of manual performance management.
Magento offers greater control over performance and scalability, making it ideal for businesses that require customization and fine-tuning while Oracle Commerce simplifies performance management with automatic scaling and a hands-off approach to infrastructure management.
Customization and Flexibility
When comparing Magento vs Oracle in terms of customization, Magento stands out for its open-source nature, offering virtually limitless customization options. Oracle Commerce Cloud, while not open-source, still provides strong customization capabilities but with more focus on pre-built integrations and enterprise-grade tools, making it easier to use for companies without dedicated development teams.
Magento
Magento is renowned for its customization options, thanks to its open-source architecture. Businesses can modify the platform’s core code, develop custom modules, and integrate third-party solutions with ease. This makes Magento one of the most flexible eCommerce platforms available, giving businesses full control over the frontend and backend of their store. Whether it’s custom checkout flows, personalized customer experiences, or integrating with external systems like ERP and CRM-s
Magento offers endless possibilities for customization. However, with this flexibility comes complexity—customizing Magento requires developer resources and ongoing technical management.
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce offers some degree of customization but within a more controlled environment. It provides integration capabilities through APIs and works seamlessly with Oracle’s suite of enterprise solutions, such as Oracle ERP and CRM systems.
Oracle Commerce is designed for businesses looking for built-in functionality and pre-configured solutions, which reduce the need for extensive custom development. While it supports personalization and custom workflows to some extent, it does not provide the same level of deep customization that Magento offers.
Oracle Commerce offers a more streamlined approach with limited customization, focusing more on seamless integration with enterprise systems.
Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
When comparing Magento vs Oracle Commerce, it’s essential to evaluate both the initial setup costs and the total cost of ownership (TCO) over time.
Magento
While Magento’s open-source version is free, running a Magento store requires significant investments in hosting, development, and maintenance. For businesses opting for Magento Commerce (Adobe Commerce Development), costs can rise steeply, with licensing fees starting at approximately $20,000 per year. On top of this, businesses will need to factor in costs for custom development, premium extensions, and advanced hosting solutions to ensure the platform performs optimally.
Due to the platform’s resource-intensive nature, robust infrastructure is required, which can also drive up costs. Magento is best suited for businesses that have the budget to invest in a highly customizable, scalable platform
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce, by contrast, operates on a subscription-based pricing model that includes cloud hosting, security, and automatic updates. While the upfront costs for Oracle Commerce may be higher, the predictability of costs makes it easier for businesses to budget.
Oracle Commerce handles infrastructure, security, and updates as part of its offering, which helps reduce the need for in-house IT resources, thus lowering the TCO in the long run compared to the self-hosted Magento option.
When it comes to costs, Oracle Commerce takes a straightforward approach with its subscription-based model. This includes hosting and regular updates, which simplifies budgeting but may limit customization options. On the flip side, Magento provides more adaptable pricing structures. However, be prepared for potentially higher expenses over time, as you’ll need to factor in technical expertise and tailored hosting solutions to keep your e-commerce platform running smoothly.
Security and Compliance
In the Magento vs Oracle Commerce debate around security, both platforms offer enterprise-level security features, but Oracle Commerce Cloud stands out with its built-in compliance and automated updates. Magento provides robust security options, but businesses must manage hosting and apply security patches manually, giving Oracle an edge for businesses seeking a hands-off approach to security management.
Magento
Magento provides advanced security features, but the responsibility for managing and maintaining these features lies with the business. Magento offers customizable security options, including PCI compliance, data encryption, and two-factor authentication. However, businesses must apply security patches, manage their own SSL certificates, and ensure that they stay on top of regular updates to protect their store from vulnerabilities.
This level of control allows businesses to tailor their security measures to meet specific regulatory and industry requirements, but it also demands dedicated resources to manage and monitor security effectively.
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce offers a more streamlined approach to security. As a cloud-hosted platform, Oracle handles automatic updates, PCI compliance, and SSL management as part of its service, making it easier for businesses to stay compliant without the need for internal IT teams to manage security manually.
Oracle Commerce’s cloud infrastructure includes built-in security features like data encryption, firewalls, and regular monitoring, ensuring a high level of protection with minimal user intervention. This hands-off approach makes Oracle Commerce an attractive option for businesses looking for robust security without the need for dedicated resources.
Magento offers customizable security features but requires businesses to manage them actively, including applying patches and updates. This approach provides flexibility but demands more resources. Oracle Commerce, on the other hand, takes a more hands-off approach by handling security measures automatically within its cloud infrastructure, making it easier for businesses to maintain compliance without extensive in-house IT involvement. The choice between the two depends on a company’s preference for control versus convenience in managing their e-commerce security.
Customer Support
For customer support, Oracle Commerce Cloud provides 24/7 enterprise-grade support, making it ideal for businesses that require dedicated assistance. Magento, while offering robust support through Adobe Commerce Cloud, also has a strong community-driven support system for its open-source version, giving businesses access to a global network of developers.
Magento
Magento offers different levels of support depending on whether you’re using Magento Open Source or Adobe Commerce. Open Source users rely primarily on the Magento community, which includes forums, documentation, and a large ecosystem of developers who share knowledge and provide solutions.
For businesses using Adobe Commerce, there’s access to 24/7 enterprise-level support, dedicated account management, and technical assistance. This support is especially useful for large businesses or enterprises with complex needs that require fast and reliable responses to any issues.
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce provides extensive support as part of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, with 24/7 support available to all users. Oracle’s support team helps manage infrastructure, updates, and technical troubleshooting.
Additionally, Oracle offers a large enterprise ecosystem that includes access to Oracle consultants, dedicated account managers, and a knowledge base for users. Oracle also has a strong partner network to assist businesses with integration and implementation needs.
Magento’s support varies between its Open Source and Adobe Commerce versions, with the former relying heavily on community forums and documentation, while the latter offers 24/7 enterprise-level support. Oracle Commerce provides comprehensive 24/7 support to all users as part of its cloud infrastructure, along with access to Oracle consultants and a partner network. The choice between the two platforms may depend on whether a business prefers community-driven support with more flexibility or a more structured, enterprise-level support system.
SEO Capabilities
In terms of SEO, Magento vs Oracle Commerce Cloud shows that Magento offers more advanced SEO customization tools with support for structured data, custom URLs, and meta tags. Oracle Commerce Cloud, while still offering strong SEO capabilities, focuses on automated optimization, providing simpler SEO tools that may appeal to businesses without the need for deep technical SEO customization.
Magento
Magento excels when it comes to SEO. It provides complete control over the optimization of product pages, URLs, meta descriptions, and tags. Magento users can customize URL structures, create sitemaps, and use built-in SEO tools to improve their store’s visibility in search engine results.
Additionally, businesses can enhance Magento’s SEO capabilities through the use of third-party extensions and plugins, making it a great option for companies that require detailed and specific SEO strategies to compete in crowded markets.
Oracle Commerce
Oracle Commerce also offers solid SEO tools, including customizable URLs, auto-generated sitemaps, and the ability to edit meta tags and descriptions. However, Oracle Commerce focuses more on out-of-the-box SEO solutions, which may not offer the same level of flexibility and control that Magento provides.
While the platform’s SEO features are robust enough for many businesses, larger enterprises with highly competitive SEO needs may find Magento’s deeper customizability more appealing.
Magento provides extensive SEO control and customization options, allowing businesses to fine-tune their optimization strategies and enhance capabilities through third-party extensions. Oracle Commerce offers solid out-of-the-box SEO tools that are sufficient for many businesses but may lack the deeper customization options of Magento. The choice between the two depends on whether a business prioritizes granular control over SEO (favoring Magento) or prefers a more streamlined, pre-configured approach (leaning towards Oracle Commerce).
Be sure to read an article where we compare Magento and Shopify.
Magento vs Oracle Commerce: A Final Side-by-Side Comparison
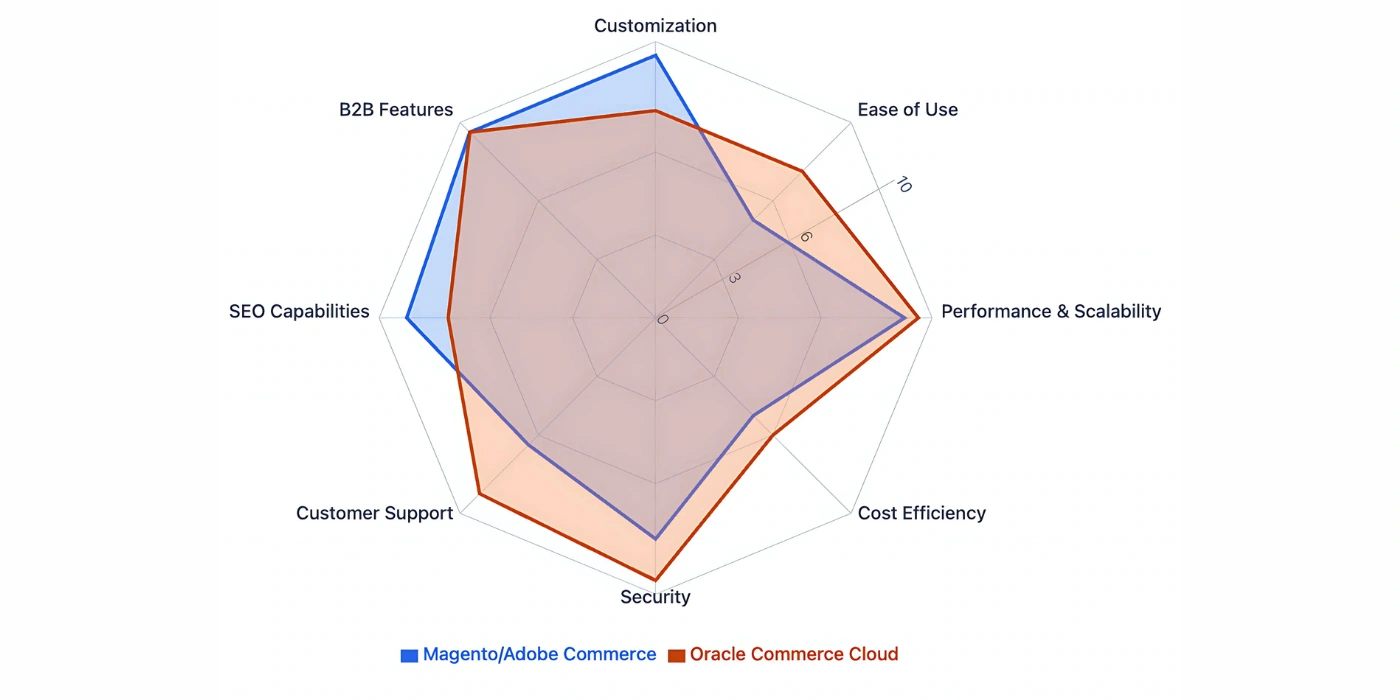
When comparing Magento and Oracle Commerce, it becomes clear that both platforms have their strengths, depending on the business’s size, technical resources, and long-term goals. Below is a comparison table to help visualize the key differences.
| Feature | Magento (Adobe Commerce) | Oracle Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Core Functionality | Highly customizable with advanced multi-store management and B2B/B2C functionality | Focused on B2B eCommerce, offering automation and seamless multi-site management |
| Ease of Use | Steeper learning curve, requires technical expertise | User-friendly interface, automation simplifies management |
| Performance & Scalability | Self-hosted, full control over optimizations | Cloud-hosted, automatic scaling and performance management |
| Customization | Full customization through open-source architecture | Limited customization, focuses on integration with enterprise systems |
| Pricing | Free Open Source; Adobe Commerce starts at around $22,000/year | Subscription-based pricing, includes cloud hosting, automatic upgrades |
| Security | Requires businesses to manage security, including patches and PCI compliance | Automatic security updates, built-in PCI compliance and SSL management |
| SEO Capabilities | Advanced SEO tools with full control and customization | Strong out-of-the-box SEO features, less flexible than Magento |
| Customer Support | Community support for Open Source; 24/7 enterprise-level support for Adobe Commerce users | 24/7 support, enterprise-level resources across all tiers |
Summary
Both Magento and Oracle Commerce offer robust solutions for large businesses, but they cater to different types of operations.
- Magento is best suited for companies that need full control over their eCommerce experience and want to build highly customized stores with advanced features. Its open-source flexibility and powerful tools make it ideal for enterprises with dedicated development teams and complex business requirements.
- Oracle Commerce, by contrast, is designed for businesses, particularly in the B2B space, that prioritize automation, ease of use, and seamless integration with other enterprise systems like ERP and CRM solutions. Oracle’s cloud-hosted infrastructure simplifies performance management, scalability, and security, making it a strong option for companies that want a hands-off approach to technical management while still benefiting from robust eCommerce tools.
At Atwix, we specialize in Magento (Adobe Commerce) implementations, helping businesses create highly customized, scalable online stores tailored to their needs. With extensive experience in delivering complex Magento solutions, our team is ready to support your business with the flexibility and power of Magento, ensuring you get the most out of this platform. If you’re looking to scale your business with Magento, contact us today to learn how we can help.
You may also want to read this: Magento Adobe Commerce VS PrestaShop
Frequently Asked Questions
Got some questions? We’re here to answer. If you don’t see your question here, drop us a line with out Contact form.
Is Magento or Oracle Commerce better for large enterprises?
Both platforms are suitable for large enterprises but cater to different needs. Magento is ideal for businesses needing extensive customization, control over their infrastructure, and multi-store management. Oracle Commerce, on the other hand, is better for enterprises focused on B2B eCommerce and seamless integration with existing enterprise systems like ERP and CRM.
How easy is it to migrate from Oracle Commerce to Magento?
Migrating from Oracle Commerce to Magento is possible but may require a technical team to ensure the transfer of product catalogs, customer data, and order histories. It involves careful planning and the use of migration tools or services from certified partners like Atwix to ensure a seamless transition.
Which platform is better for B2B eCommerce, Magento or Oracle Commerce?
Oracle Commerce is generally better suited for B2B eCommerce due to its strong automation features and seamless integration with enterprise systems. Magento is also strong in B2B capabilities, offering extensive customization, but Oracle Commerce is more tailored to businesses prioritizing automated workflows and large-scale operations.
Which platform offers better SEO tools, Magento or Oracle Commerce?
Magento provides more advanced and customizable SEO tools, allowing businesses to optimize URLs, meta tags, and schema markup. Oracle Commerce offers strong out-of-the-box SEO features, but it lacks the depth of customization Magento provides, making Magento a better choice for businesses with highly competitive SEO strategies.
Is Oracle Commerce as flexible as Magento when it comes to customization?
No, Oracle Commerce is more limited in customization compared to Magento. While Oracle Commerce focuses on ease of use and integration with enterprise systems, Magento offers deeper customization capabilities through its open-source architecture, allowing businesses to modify almost every aspect of their store.

