When choosing between Magento vs WooCommerce, the right eCommerce platform depends on the complexity and scale of your business. Magento (Adobe Commerce) is widely recognized for its powerful scalability and customization options, making it the preferred choice for larger enterprises with sophisticated eCommerce needs. It excels in handling complex operations such as multi-store setups, global sales, and B2B solutions.

On the other hand, WooCommerce is a WordPress plugin that offers flexibility and ease of use for small to medium-sized businesses. This fundamental difference between Magento vs WooCommerce becomes especially important when considering your technical resources and growth plans. Its integration with WordPress allows for quick setup and an intuitive interface, making it ideal for businesses with less technical expertise. If your business is already running on WordPress, WooCommerce provides a seamless way to add eCommerce functionality.
Choosing the right platform—Magento or WooCommerce—will depend on your business’s specific needs, whether you prioritize extensive customization and scalability or simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Let’s explore this Magento vs WooCommerce comparison in detail to help you make an informed decision
Key Differences Between Magento and WooCommerce
Core Functionality: Magento vs WooCommerce Comparison
When evaluating the core features of Magento vs WooCommerce, their differing approaches become clear: Magento is designed for handling complex, large-scale eCommerce operations, while WooCommerce is built to provide a user-friendly solution for smaller businesses that want to quickly and easily integrate eCommerce into their WordPress site. This fundamental difference shapes how businesses approach the Magento vs WooCommerce decision from a functionality standpoint.
Magento’s Enterprise-Grade Features
Magento (Adobe Commerce) excels in offering a wide range of advanced features for both B2B and B2C businesses. It provides multi-store management, meaning businesses can manage multiple stores, currencies, and languages from a single backend—a crucial feature for companies with global ambitions. Magento also boasts advanced inventory management, which allows businesses to handle complex product catalogs efficiently.
Through the Magento Marketplace, businesses can integrate third-party solutions, including shipping modules, marketing tools, and payment gateways. The flexibility of Magento’s platform enables custom workflows and checkout processes, which is especially important for companies that need tailored solutions for their unique customer journeys.
WooCommerce’s WordPress Integration
As a WordPress plugin, WooCommerce is built to integrate easily with existing WordPress sites. Its core features cover essential eCommerce functionalities, including product management, inventory tracking, order processing, and shipping options. For businesses already using WordPress, WooCommerce provides a familiar interface that makes it easy to add products, manage payments, and handle customer orders.
WooCommerce’s ecosystem allows users to expand their store’s functionality through various plugins, including SEO tools, marketing integrations, and shipping extensions. However, while WooCommerce offers flexibility, it lacks some of the out-of-the-box advanced features that Magento provides, especially for large, complex eCommerce operations.
Magento is a more powerful platform, offering extensive customization and features designed for large enterprises that need to manage complex product catalogs and multiple stores. In contrast, WooCommerce is a simpler solution ideal for small to medium-sized businesses already running on WordPress. It offers essential eCommerce tools but relies on additional plugins to reach the level of customization that Magento provides.
User Experience: Comparing Magento and WooCommerce Interfaces
In terms of ease of use, Magento vs WooCommerce have stark differences. Magento is known for its power but requires more technical expertise, whereas WooCommerce is user-friendly and caters to non-developers, especially those familiar with WordPress.
Magento’s Admin Dashboard
Magento is designed for businesses that have development resources or teams with technical expertise. Its complexity stems from the vast range of customization options available for storefronts, checkout flows, and integrations. While the platform allows for complete control over the store’s design and functionality, the interface can be overwhelming for non-technical users.
Managing features like multi-store setups, inventory, and custom workflows requires a solid understanding of the platform and, in many cases, a dedicated development team. Despite this complexity, Adobe Commerce Cloud simplifies some of the setup processes by offering cloud-based hosting, but technical management is still required for deep customizations.
WooCommerce’s User-Friendly Controls
WooCommerce shines in its ease of use, particularly for users who are already familiar with WordPress. It integrates seamlessly with WordPress, making the setup process straightforward, with guided wizards helping users configure payment gateways, taxes, and shipping options. WooCommerce’s interface is intuitive, allowing users to manage products, orders, and customers without needing extensive technical knowledge.
The block-based editor used in WooCommerce makes it easy for non-developers to create and manage their store, making it a top choice for small businesses or startups looking for a simple solution.
For businesses that prioritize ease of use, WooCommerce is the better choice. Its integration with WordPress makes it incredibly intuitive for non-technical users. In contrast, Magento is more powerful but requires a higher level of technical expertise and is better suited for businesses with in-house developers or those working with Magento partners. When conducting a Magento vs WooCommerce user interface evaluation, this difference in learning curve should be a primary consideration.
Performance and Scalability: Handling Business Growth
When comparing Magento vs WooCommerce in terms of performance and scalability, both platforms offer the potential to grow with your business, but the level of effort required to achieve optimal performance varies significantly.
Magento’s Enterprise Scalability
Magento is known for its ability to scale for large, complex eCommerce operations. It can handle massive product catalogs, high traffic volumes, and complex store setups with ease. Magento’s scalability makes it the platform of choice for businesses that expect rapid growth or need to manage multiple stores and regions. However, Magento Open Source users must manage their own hosting, meaning performance depends on the quality of the hosting provider and how well the platform is optimized.
For businesses using Adobe Commerce Cloud, scalability becomes much easier, as Magento’s cloud infrastructure takes care of hosting and performance optimizations. That said, technical expertise is still required to fine-tune performance, including caching, CDNs, and server optimization.
WooCommerce’s Performance Capabilities
WooCommerce performs well for small to medium-sized stores, but its scalability depends largely on the WordPress hosting environment and plugins used. As WooCommerce stores grow, store owners need to invest in optimized hosting solutions to handle high traffic and large product catalogs. While WooCommerce can scale, performance may suffer if the site isn’t properly optimized with tools like caching plugins, CDNs, and performance-enhancing extensions.
WooCommerce is well-suited for businesses that plan to scale at a moderate pace, but for large-scale operations, it may require frequent performance optimizations as the business grows.
Magento is built for large-scale businesses that expect high traffic and complex operations. It provides scalability without compromising performance, especially when using Adobe Commerce Cloud. In a WooCommerce vs Magento comparison of performance at scale, WooCommerce requires more effort to maintain optimal speeds as the store grows, making it ideal for small to medium-sized businesses with moderate traffic expectations.
Customization and Flexibility: Development Options
When comparing Magento vs WooCommerce, both platforms offer excellent flexibility for customizing your online store. Each platform approaches customization differently though – Magento provides deeper technical control that enterprises value, while WooCommerce vs Magento offers a more accessible plugin-based approach that many small to mid-sized businesses find easier to manage.
Magento’s Extensive Customization Framework
Magento is highly customizable, offering unparalleled control over the frontend and backend of the store. It’s an open-source platform, which means businesses can modify every part of the store’s design, functionality, and workflow. The Magento Marketplace is filled with thousands of extensions that allow businesses to integrate additional features like advanced analytics, marketing tools, payment gateways, and shipping solutions.
For businesses with in-house development teams or access to Magento-certified developers, the platform provides the flexibility to build complex custom features, personalized customer experiences, and multi-store setups. The open-source nature of Magento makes it perfect for enterprises needing tailored solutions, but it requires ongoing development and management.
WooCommerce’s Plugin Ecosystem
WooCommerce also offers strong customization options, especially for businesses already using WordPress. Through the WordPress plugin ecosystem, WooCommerce users can enhance their stores with a wide range of plugins for payments, shipping, marketing, and more. Themes and page builders allow for flexible design customization without requiring deep coding knowledge.
However, while WooCommerce is flexible, it doesn’t offer the same level of backend customization as Magento. For more complex customizations, WooCommerce users may need to rely on third-party developers or advanced plugins.
Magento offers unlimited customization for businesses with specific needs, making it the top choice for enterprises looking for a completely customized eCommerce experience. WooCommerce, while flexible, is more reliant on the WordPress plugin ecosystem and may not offer the same level of backend customization as Magento. Many businesses find that this WooCommerce vs Magento customization difference is a deciding factor when making their final platform choice.
Pricing Comparison: Total Cost of Ownership
When evaluating Magento vs WooCommerce based on pricing, it’s important to consider not only the initial setup costs but also the long-term maintenance and development expenses.
Magento’s Pricing Structure
While Magento’s open-source version is free, running a Magento store requires significant investments in hosting, development, and maintenance. For businesses opting for Magento Commerce (Adobe Commerce Development), costs can rise steeply, with licensing fees starting at approximately $22,000 per year. On top of this, businesses will need to factor in costs for custom development, premium extensions, and advanced hosting solutions to ensure the platform performs optimally.
Due to the platform’s resource-intensive nature, robust infrastructure is required, which can also drive up costs. Magento is best suited for businesses that have the budget to invest in a highly customizable, scalable platform
WooCommerce’s Cost Breakdown
WooCommerce is also free as a WordPress plugin, but additional costs come from hosting, plugins, and premium themes. WooCommerce stores generally have lower upfront costs than Magento, but businesses may need to invest in premium plugins or extensions to achieve the level of functionality they require.
Hosting costs for WooCommerce can also vary, but they are typically lower than Magento’s, especially for smaller businesses. WooCommerce’s overall cost structure makes it a more affordable solution for small to medium-sized businesses, but as the store grows, the cost of plugins and performance optimization may add up.
Magento offers a more flexible pricing model but typically has higher ongoing costs due to the need for custom development, hosting, and security. WooCommerce, while more budget-friendly for smaller stores, may require additional investments in plugins and hosting as the store scales.
You can also read this comparison article: Magento Adobe Commerce VS BigCommerce.
Security and Compliance: Protecting Your Online Store
When comparing security features between Magento vs WooCommerce, businesses will find distinct approaches to protecting their online stores. Magento delivers enterprise-grade security with robust built-in protections, while WooCommerce vs Magento relies more on WordPress’s security framework and third-party plugins. Your business requirements should determine which platform’s security model makes more sense for your specific situation.
Magento’s Security Features
Magento has built-in security features designed to handle enterprise-level security needs, including PCI compliance, SSL certificates, and regular security patches. For businesses using Adobe Commerce Cloud, security updates and patches are automated, providing an added layer of protection. Magento also supports two-factor authentication (2FA) and offers advanced security extensions that help businesses secure their online stores from threats.
Since Magento is often used by larger enterprises, its security features are designed to support high-traffic, high-value eCommerce operations, providing customizable options to meet specific compliance needs.
WooCommerce’s Security Solutions
While WooCommerce itself is secure, it is dependent on WordPress and its broader ecosystem for security. WordPress is known for its vulnerabilities, often arising from outdated plugins or themes. Businesses using WooCommerce need to ensure that their WordPress installation, plugins, and themes are regularly updated to maintain security.
WooCommerce users can also install security plugins like Wordfence to add additional layers of protection. However, the responsibility for maintaining security largely falls on the store owner, which can be challenging for businesses without dedicated technical support.
Magento is a more secure platform out of the box, with dedicated security patches and support for enterprise-level compliance, making it the preferred choice for larger businesses. WooCommerce, while secure, requires more manual oversight and regular updates to maintain security, relying heavily on third-party plugins and hosting providers.
Support Resources: Available Help and Documentation
Looking at support options between Magento vs WooCommerce, each platform serves businesses differently. Magento provides enterprise-level support through Adobe and its partner network, while WooCommerce offers community-based assistance through the WordPress ecosystem. Your business needs will determine which support system works better for yo
Magento’s Support Ecosystem
Magento has a massive, global community of developers, users, and certified partners, making it easy to find support, tutorials, and solutions to common issues. For Magento Open Source users, most support comes from community forums, documentation, and online resources, making it a more DIY experience. However, Adobe Commerce Cloud users have access to 24/7 support, dedicated account managers, and enterprise-grade assistance, including help with custom integrations and performance optimizations.
Magento also offers a vast network of certified development partners who provide professional services for businesses that need expert help with their store.
WooCommerce’s Community Support
WooCommerce is backed by the WordPress community, which is one of the largest and most active online communities. Users have access to numerous forums, tutorials, and third-party support from plugin developers.
However, WooCommerce itself does not offer direct support. Instead, businesses often rely on their WordPress hosting providers for WooCommerce-specific support. Many managed WordPress hosting services offer dedicated WooCommerce support plans, which can simplify store management for businesses without technical teams.
Magento offers more enterprise-level support through Adobe Commerce Cloud, while WooCommerce provides community-driven support with third-party plugin and hosting assistance. For businesses needing dedicated account managers and 24/7 support, Magento is the superior choice, while WooCommerce is more reliant on its broad WordPress ecosystem.
SEO Capabilities: Ranking Potential Comparison
When comparing Magento vs WooCommerce for SEO capabilities, both platforms offer strong tools to help your store rank well, though they approach search optimization differently. Magento provides more built-in technical SEO features, while WooCommerce leverages WordPress’s SEO-friendly foundation and popular plugins.
Magento’s SEO Tools
Magento provides advanced SEO tools out of the box, allowing businesses to optimize meta tags, URLs, sitemaps, and structured data. With built-in support for rich snippets, mobile optimization, and SEO-friendly URLs, Magento ensures that businesses can rank higher in search engines.
Additionally, Magento allows for more granular control over technical SEO elements, making it ideal for businesses that rely heavily on organic search traffic. Third-party SEO extensions can also be added from the Magento Marketplace to enhance its SEO capabilities further.
WooCommerce’s WordPress SEO Advantages
WooCommerce inherits much of its SEO power from WordPress, which is inherently SEO-friendly. Through plugins like Yoast SEO and Rank Math, WooCommerce users can easily optimize their product pages, URLs, and meta descriptions.
While WooCommerce’s out-of-the-box SEO capabilities may not be as advanced as Magento’s, the range of available SEO plugins makes it easy to implement effective SEO strategies without needing deep technical expertise. WordPress’s strong SEO foundation makes WooCommerce highly customizable for SEO-focused businesses.
Magento offers advanced, built-in SEO features, making it the better option for businesses with complex SEO needs. WooCommerce, while more reliant on third-party plugins like Yoast SEO, is also highly SEO-friendly, thanks to its integration with WordPress.
Be sure to read an article where we compare Magento and Shopify.
Magento vs WooComerce: A Final Side-by-Side Comparison
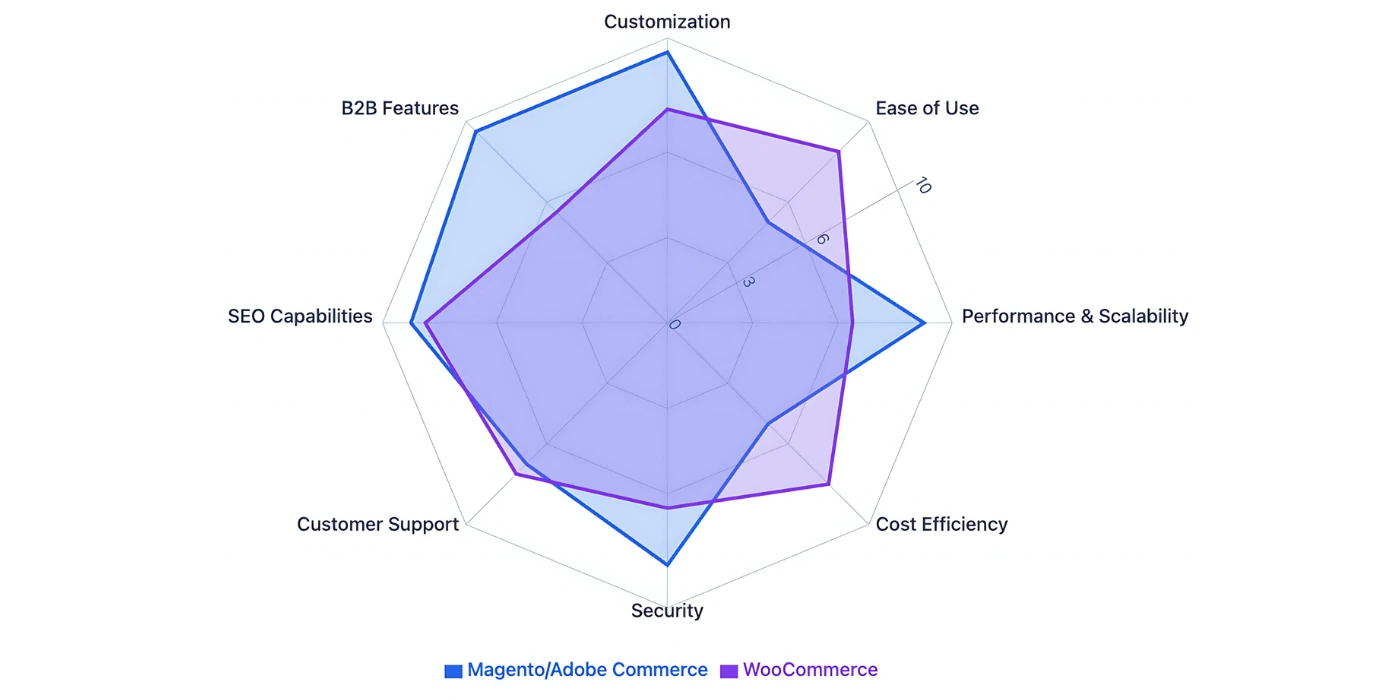
When choosing between Magento vs WooCommerce, it’s important to recognize that these two platforms serve different types of eCommerce businesses. While both offer flexibility and scalability, the depth of features, ease of use, and long-term cost of ownership set them apart. Here’s a final comparison to help guide your decision:
| Feature | Magento (Adobe Commerce) | WooCommerce |
|---|---|---|
| Core Functionality | Advanced features for complex stores, multi-store management, and B2B support | Basic features, expandable via plugins, ideal for SMBs |
| Ease of Use | Steep learning curve, requires technical expertise | User-friendly, especially for WordPress users |
| Performance & Scalability | Highly scalable, requires optimized hosting for large operations | Performance depends on hosting, scales with plugins |
| Customization | Unlimited customization via open-source flexibility, high level of control | Flexible through plugins, limited backend customization |
| Pricing | Free open-source, but high hosting and development costs | Free plugin, but additional plugins and hosting needed |
| Security | High-level security, dedicated patches and PCI compliance | Relies on WordPress plugins, requires regular updates |
| SEO Capabilities | Advanced SEO tools built into the platform | SEO-friendly with WordPress, relies on plugins like Yoast SEO |
| Customer Support | 24/7 support for Adobe Commerce Cloud, extensive community for Open Source | Community-driven support with WordPress, third-party hosting support |
Which Platform Should You Choose? Decision Framework
In the Magento vs WooCommerce debate, choosing the right platform depends on the size, complexity, and long-term goals of your business.
- Magento (Adobe Commerce) is perfect for large-scale businesses or enterprises with complex needs, such as multi-store management, B2B operations, and custom features.** It offers extensive scalability and flexibility through its open-source architecture, making it suitable for businesses that require highly tailored solutions. However, it comes with higher costs due to the need for technical expertise, hosting, and ongoing development, making it best for businesses with the resources to manage these complexities.
- WooCommerce, as a WordPress plugin, is an excellent choice for small to medium-sized businesses. It offers easy integration with WordPress, is user-friendly, and has lower upfront costs. For businesses already familiar with WordPress, WooCommerce provides an easy way to add eCommerce functionality without needing extensive technical support. However, as your business grows, the reliance on third-party plugins for advanced features and performance optimization may increase costs over time.
You may also want to read this: Magento Adobe Commerce VS PrestaShop and this too: Magento VS Oracle Commerce Cloud.
Frequently Asked Questions
Got some questions? We’re here to answer. If you don’t see your question here, drop us a line with out Contact form.
Which platform is better for small businesses: Magento or WooCommerce?
WooCommerce is generally better for small businesses. It is easier to use, integrates seamlessly with WordPress, and has lower upfront costs. For businesses already using WordPress, WooCommerce offers a straightforward and cost-effective way to add eCommerce functionality. Magento, while more powerful, is designed for larger businesses with complex operations and requires more technical expertise to manage.
Is Magento more customizable than WooCommerce?
Yes, Magento is more customizable than WooCommerce. Magento’s open-source architecture allows for deep backend customization, from product management to checkout processes. It is designed for businesses that need full control over their eCommerce operations. WooCommerce, while also customizable, relies heavily on WordPress plugins for added functionality and may not offer the same level of backend customization as Magento.
How does the pricing of Magento compare to WooCommerce?
Magento Open Source is free to download, but businesses must cover the costs of hosting, security, and development, which can add up, especially for larger stores. Adobe Commerce Cloud starts at around $22,000 per year, making it more expensive for enterprises. WooCommerce, as a WordPress plugin, is also free, but businesses need to account for hosting, premium plugins, and security plugins. In general, WooCommerce is more affordable upfront, but costs can increase as the store grows and requires more plugins or optimizations.
Which platform offers better scalability: Magento or WooCommerce?
Magento offers better scalability for large enterprises. It can handle high traffic volumes, large product catalogs, and complex store setups with ease. WooCommerce, while scalable, requires significant performance optimizations as the store grows, including investments in optimized hosting and caching plugins. Magento’s infrastructure is designed for businesses expecting rapid growth, while WooCommerce is better suited for smaller stores scaling at a moderate pace.
Which platform is better for SEO: Magento or WooCommerce?
Both platforms offer strong SEO capabilities, but in different ways. Magento provides built-in SEO tools and allows for deep customization of meta tags, URLs, and sitemaps, making it ideal for businesses with advanced SEO needs. WooCommerce, being built on WordPress, leverages SEO plugins like Yoast SEO, which makes it easier for non-technical users to optimize their stores for search engines. WooCommerce is better suited for businesses that need simple, plugin-driven SEO solutions, while Magento offers more comprehensive, built-in SEO tools.

